Antivenom
A guide to antivenom & alpha-gal syndrome (AGS)
Alpha-gal syndrome
and antivenom
Responding to
venomous snake bites
Select publications
on AGS and antivenom
Alpha-gal syndrome and antivenom
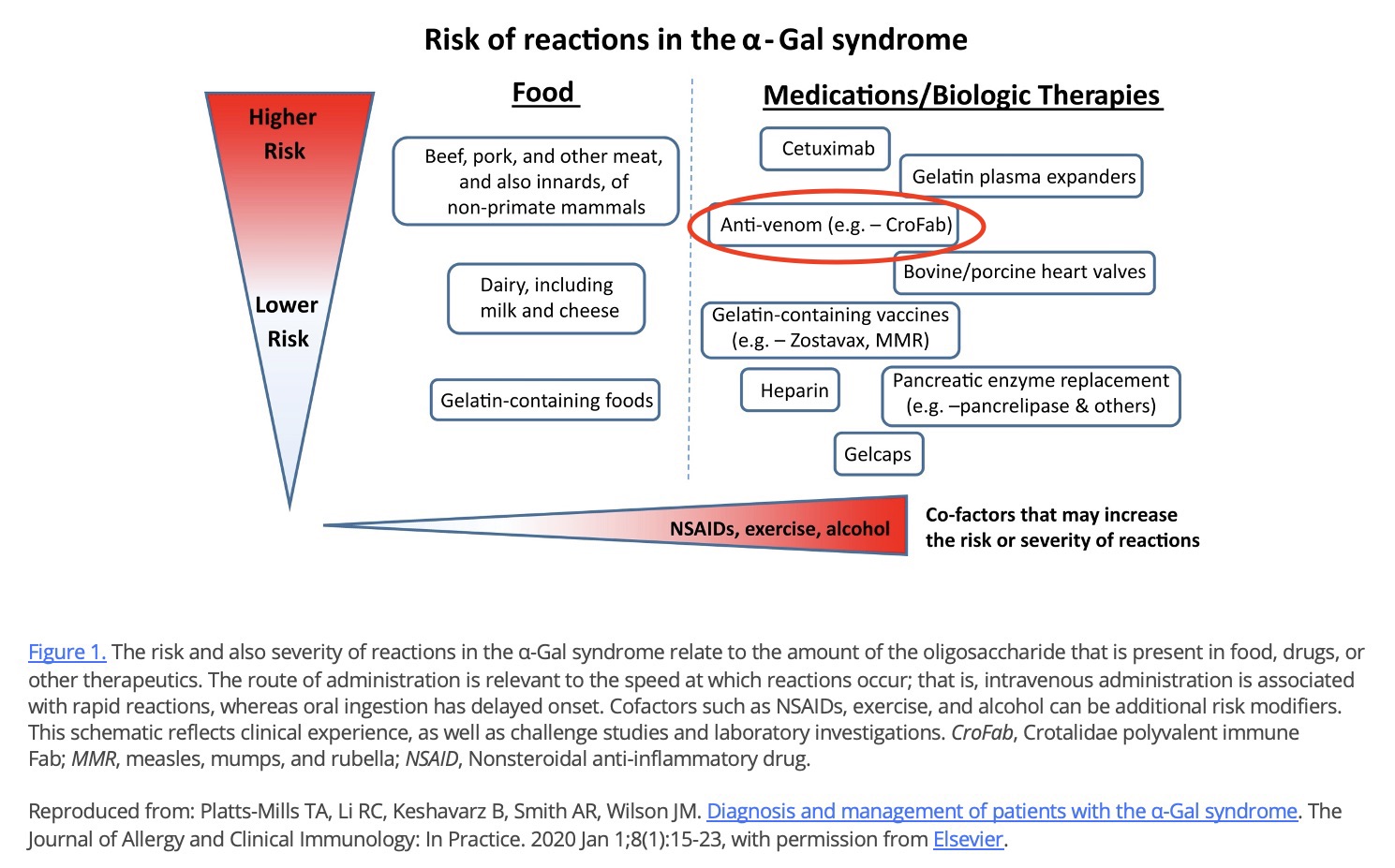
Anti-venom: Alpha-gal is present in anti-venom formulations because these purified fragments are derived from venom-immunized non-primate mammals. There has been at least one case report of an acute reaction to CroFab in a patient with AGS. Despite this report, we advise administration of CroFab if clinically indicated even in patients with AGS as the risk of reaction to anti-venom has not been established in this scenario and may be quite low while, on the contrary, the therapeutic benefit of anti-venom is high.
Antivenoms are produced in horses and sheep (nonprimate mammals) as polyclonal IgG preparations. Previous studies have reported IgE to a-GAL and increased rates of hypersensitivity reactions to Fab administration. Investigators noticed higher rates of hypersensitivity reactions to Fab in Virginia compared to Arizona, where a-GAL sensitization would be rare because it lacks the tick A. americanum. An abstract from the manufacturer of Fab shows that both Fab and F(ab’)2 antivenoms contain a-GAL. Quantitative analysis of the western blots suggested approximately 3-fold more a-GAL was present on F(ab’)2 compared to Fab antivenom per unit weight.
—————————————————-
In this study, we demonstrate a high frequency of adverse drug reactions (37.8%) and presumed anaphylaxis (21.6%) in subjects receiving F(ab’)2 in Arkansas. Other national and regional studies (specifically from the southwestern United States) report that 0 to 2.5% of patients receiving F(ab’)2 experienced immediate hypersensitivity reactions.2,3 Our data also indicate that 5.9% of the subjects had any adverse drug reaction to the Fab antivenom. These findings align with those from Virginia, Arkansas, and Oklahoma, all states with high rates of a-GAL sensitization.
————————————————
Notably, subjects with adverse drug reactions to snake antivenom with IgE testing available in the poison control narratives were all positive for a-GAL.
————————————————
However, the relationship between adverse drug reaction propensity and severity remains unclear. Only 1 subject with a positive IgE for a-GAL had a history of allergic responses to red meat. The other 4 subjects with a positive IgE for a-GAL and adverse drug reactions to F(ab’)2 or Fab were reportedly consuming red meat without symptoms.
————————————————
These data suggest that exposure to a-GAL antigen in the bloodstream (through intravenous injection) could cause anaphylaxis, even when oral exposure to red meat does not occur.
————————————————
In conclusion, our findings demonstrate a high rate of adverse drug reactions and presumed anaphylaxis to crotaline antivenoms in an area where a-GAL IgE sensitization is common. In our cohort, reactions to F(ab’)2 were more common than for Fab antivenoms, but more work is needed with prospective studies to evaluate these outcomes. Although administering antivenoms remains essential in managing some snake envenomations, clinicians practicing in a-GAL endemic regions may wish to exercise increased vigilance and prepare for adverse drug reactions and anaphylaxis, especially when treating patients with a history of red meat allergy.
Both the presence of alpha-gal in some snake antivenom, such as crotalidae polyvalent immune Fab (CroFab) and Anavip® (6,50,51,57,104), and its association with severe reactions in patients with alpha-gal syndrome have been established (6,50,51,57, 104).
If an envenomation requires antivenom, National Snakebite Support recommends that you treat with antivenom, even if the patient has alpha-gal syndrome.
Crofab® vs Anavip®
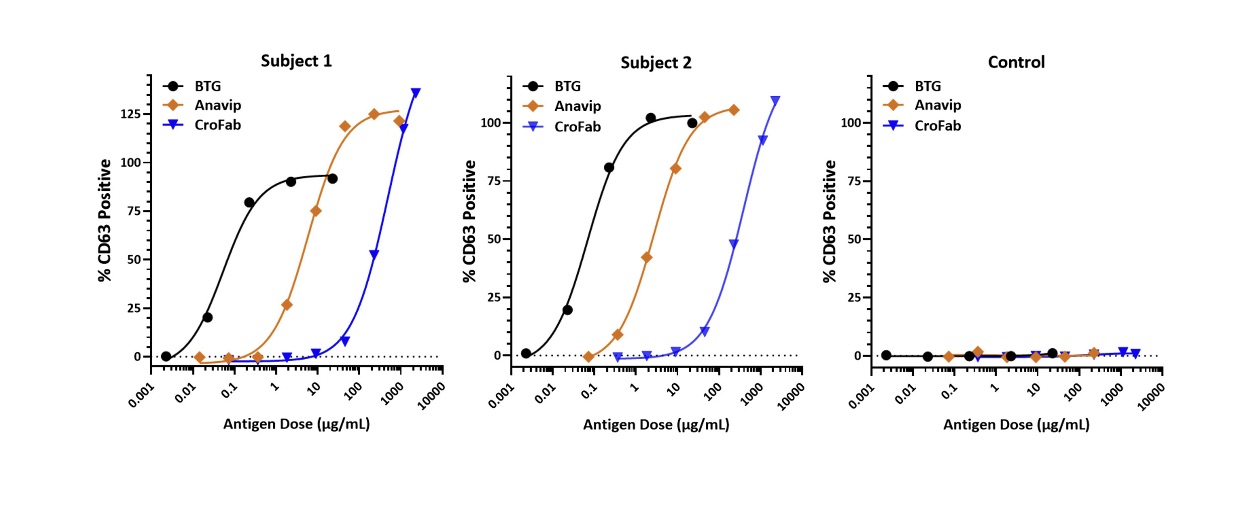
Basophil activation test results from 2 subjects with α‐gal syndrome and one non‐allergic control. Basophils were exposed, ex vivo, to bovine thyroglobulin (BTG; serially diluted 1:10 from 100 to 0.01 μg/mL), or to the antivenom biologics Anavip (diluted 1:5 from 1000 to 0.32 μg/mL) or CroFab (diluted 1:5 from 10,000 to 1.6 μg/mL). Flow cytometry was used to detect the percentage of CD63‐positive basophils (a measure of basophil activation). The % CD63 positive data were normalized based on the anti‐FcεRI positive control (100%) and baseline negative control (stimulation buffer; 0%).
Source: Platts-Mills TAE, Gangwar RS, Workman L, Wilson JM. The immunology of alpha-gal syndrome: History, tick bites, IgE, and delayed anaphylaxis to mammalian meat. Immunol Rev. 2025;332(1):e70035.
Geographic considerations
Excerpts from McKnight M, Mullins ME. Fab or F (ab’) 2 Antivenom: Which Should we use for North American Crotalids?. Journal of Medical Toxicology. 2025 Sep 18:1-3.:
Glaser et al. compare acute hypersensitivity reactions (AHR) of each antivenom. They found rates of AHR to be twice as high with F(ab’)2 (6.2%) compared to Fab (2.9%). However, in states with highest prevalence of alpha gal syndrome (Arkansas, Kentucky, Missouri, Oklahoma, and Virginia) [5], the AHR rate was nearly seven times higher with F(ab’)2 (22.2%) than with Fab (3.3%). This disparity is similar to that reported by Greene and Teshon in southeastern Texas [6]. They found that adverse events (AEs) were about four times more frequent in the F(ab’)2 group (14.7%) compared to the Fab group (3.8%). The low rates of AEs with Fab seen in both studies are comparable to rates in previous studies [7–9].
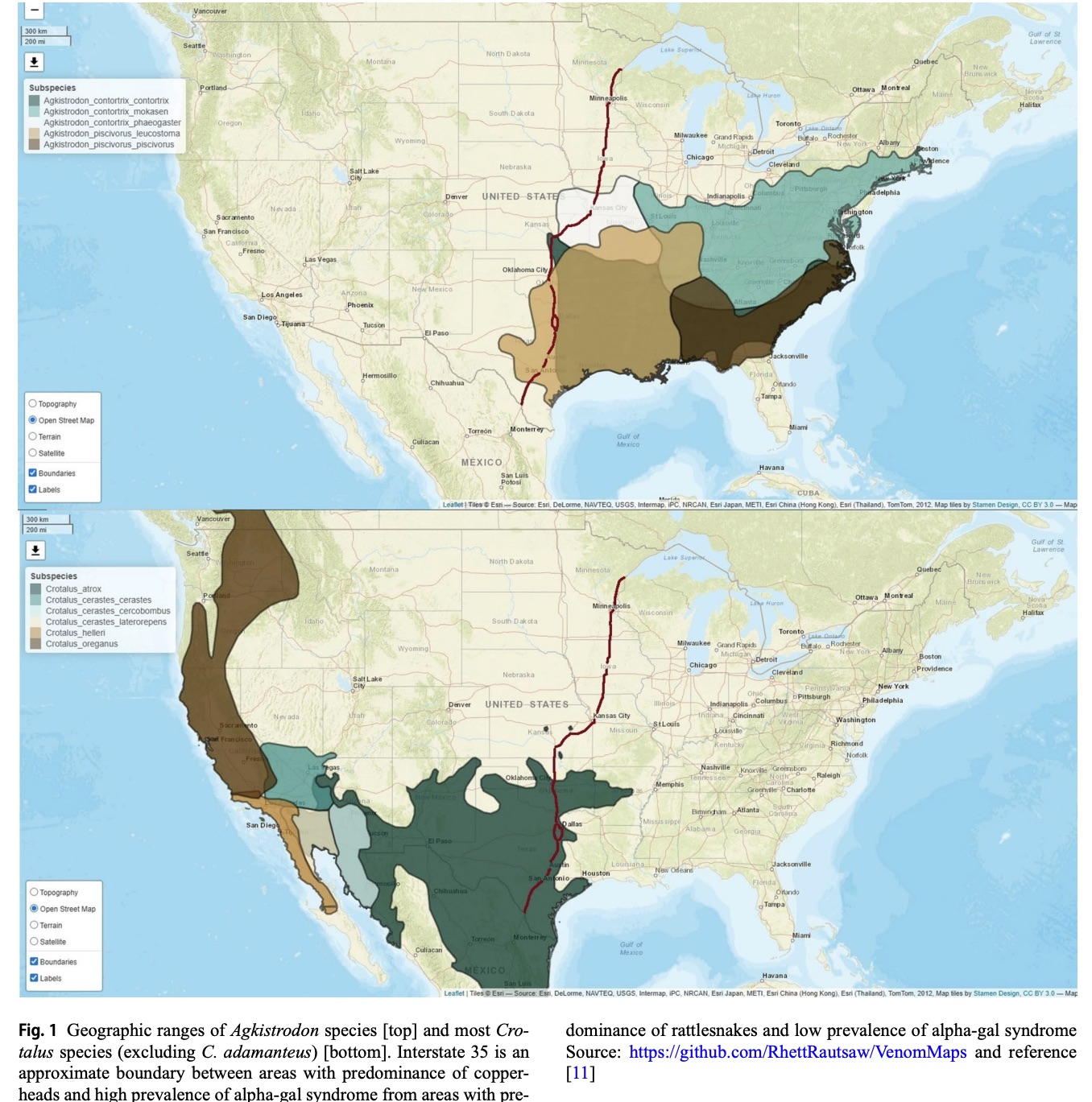
We perceive that F(ab’)2 is now the preferred AV In the desert Southwest, where rattlesnakes predominate and alpha-gal syndrome is rare. The cost [1] and the prevention of delayed coagulopathy [10] appear to justify tolerating modestly higher rate of AHS. However, in the Southeast, where both copperheads and alpha-gal abound, the lower cost [1] and the much lower rate of AHS favors Fab. Where should we draw the line between regions?
We suggest that Interstate 35 (I-35) is a reasonable and recognizable boundary. I-35 bisects the continental United States from Duluth, Minnesota to Laredo, Texas. I-35 roughly separates the geographic ranges of most copperheads and most rattlesnakes (Fig. 1) [11]. Considering these cost and safety factors, we suggest that if one is east of I-35 then one should probably use Fab and if one is west of I-35 then one should use F(ab’)2. This may work until snakes start driving on the wrong side of the road.
Responding to venomous snake bites
If an envenomation requires antivenom, you treat with antivenom. There is no absolute contraindication.
All antivenoms have alpha-gal to some extent. We have two options when treating an AGS patient with antivenom. We can monitor really carefully and treat if/when signs and symptoms develop, or we can pre-medicate with antihistamines +/- steroids with epinephrine available. You never want to withhold antivenom when it is really necessary. We can treat an allergic reaction.
In the event of a venomous snake bite, contact the National Snakebite Support. National Snakebite Support™ (NSS) connects snakebite victims and healthcare providers with experts who practice and promote evidence-based snakebite management. NSS is familiar with management of snake bites in patients with AGS.
Select publications
on AGS and antivenom
Updated Oct 31, 2025
- McKnight M, Mullins ME. Fab or F (ab’) 2 Antivenom: Which Should we use for North American Crotalids?. Journal of Medical Toxicology. 2025 Sep 18:1-3.
- Dart RC. Snake antivenom reactions: A new finding and continued controversy. Ann Emerg Med. 2025;0(0). doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2025.09.023
- Glaser T, Culbreth R, Liebelt EL, et al. Analysis of acute hypersensitivity reactions by antivenom type and geographic location in the north American snake bite registry (NASBR). J Med Toxicol. 2025;21(3):312-319.
- Filip AB, Mahmood L, Tilly C, Foster HR, Jackson F, Banner W, Platts-Mills TAE, Wilson J, Bortz PS, Charlton N, Kennedy JL. Prevalence of Adverse Drug Reactions: Comparing Crotalidae Immune Polyvalent Antivenoms F(ab’)2 and F(ab) in a Galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose (alpha-gal) Endemic Area. Ann Emerg Med. 2025 Aug 16:S0196-0644(25)01039-X. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2025.06.618. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40817895.
- Banner W, Edelen K, Epperson LC, Moore E. Hypersensitivity reactions due to North American pit viper antivenom administration and confirmed elevation of alpha-gal IgE. Toxicology Communications. 2024;8(1):2314314.
- Greene S, Teshon A. Acute adverse reactions in two pit viper antivenoms. Toxicol Commun. 2024;8(1):2395687.
- Wai M, Filip AB, Abbott A, Martin A, Donnell R, Sutton J. Anaphylaxis in Alpha-Gal patients treated with F(ab’) 2 for snake bite venom. Toxicol Commun. 2024;8(1). doi:10.1080/24734306.2024.2392459
- Blessmann J, Hanlodsomphou S, Santisouk B, et al. Serum IgE against galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose is common in Laotian patients with snakebite envenoming but not the major trigger for early anaphylactic reactions to antivenom. Toxicon X. 2020;7:100054.
- Straesser M, Keshavarz B, Borish L, et al. α-Gal on Crotalidae-polyvalent Fab antivenom (CroFab): Investigating the relevance to immediate hypersensitivity reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9(2):1015-1017.e1.
- Rizer J, Brill K, Charlton N, King J. Acute hypersensitivity reaction to Crotalidae polyvalent immune Fab (CroFab) as initial presentation of galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose (alpha-gal) allergy. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2017;55(7):668–9.
- Fischer J, Eberlein B, Hilger C, Eyer F, Eyerich S, Ollert M, et al. Alpha-gal is a possible target of IgE-mediated reactivity to antivenom. Allergy. 2017;72(5):764–71.
- Filip A, Kennedy J, Wilson J, et al. Disparity in immune-mediated reactions to Crotalidae polyvalent immune fab (ovine) and Crotalidae immune F (ab’) 2 [equine] in alpha-gal endemic regions and alpha-gal sensitized adults. In: CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY. Vol 62. TAYLOR & FRANCIS LTD 2-4 PARK SQUARE, MILTON PARK, ABINGDON OR14 4RN, OXON …; 2024:5-5.
- Platts-Mills TAE, Gangwar RS, Workman L, Wilson JM. The immunology of alpha-gal syndrome: History, tick bites, IgE, and delayed anaphylaxis to mammalian meat. Immunol Rev. 2025;332(1):e70035.