Vaccines
A guide to vaccines & alpha-gal syndrome (AGS)
AGS & vaccines
Gelatin &
Vaccines
Graded dosing
More info
Publications
Alpha-gal syndrome and vaccines
Guidance for patients with AGS: should not receive vaccines with gelatin, if possible.
__________
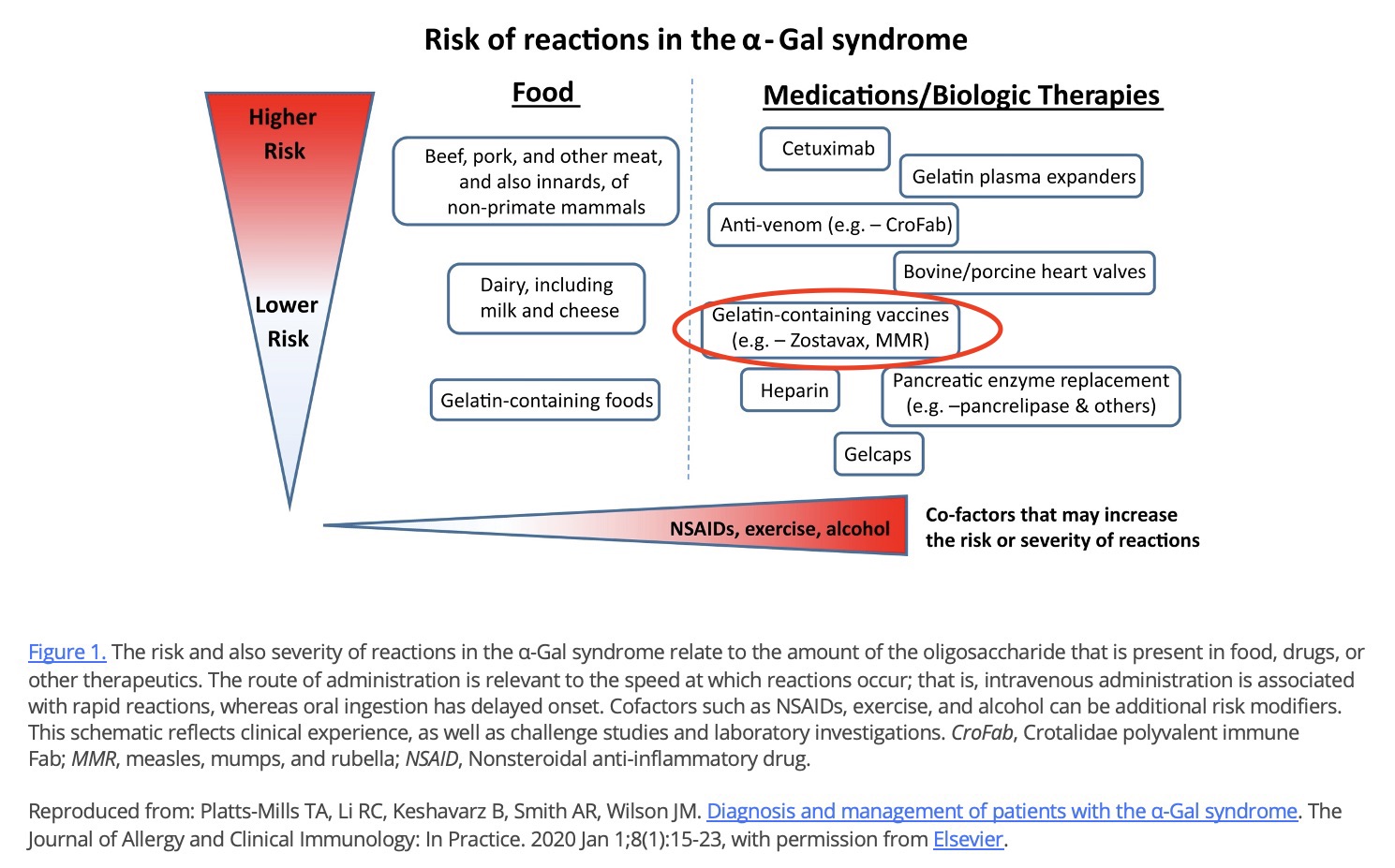
Vaccines are also an important source of gelatin exposure, including Zostavax and MMR. Cases of reactions to these vaccines in patients with alpha-gal IgE have been reported.
Gelatin is present in some vaccines, including Zostavax and MMR. Cases of reactions to these vaccines in patients with IgE to α-Gal have been reported.
Animal-derived products used in vaccine manufacture can include amino acids, glycerol, detergents, gelatin, enzymes and blood. Cow milk is a source of amino acids, and sugars such as galactose. Cow tallow derivatives used in vaccine manufacture include glycerol. Gelatin and some amino acids come from cow bones. Cow skeletal muscle is used to prepare broths used in certain complex media. Many difficult to grow microorganisms and the cells that are used to propagate viruses require the addition of serum from blood to the growth media.
Some vaccines contain gelatin, and there are published reports of alpha-gal-related reactions to gelatin-containing vaccines.
Experts recommend that people with AGS avoid vaccines that contain gelatin when possible. When a provider deems that the potential benefits of a gelatin-containing vaccine outweigh the potential risks, precautions such as premedication, graded dosing, and medical supervision may be considered.
In addition to gelatin, vaccines may contain other mammal-derived excipients or residual traces of mammal-derived ingredients used in the manufacturing process. Other vaccines are made in mammalian cell lines. There is a lack of data on the risk of reactions associated with these vaccines.
Boostrix and Flucelvax are two vaccines that do not contain gelatin but may be best avoided by patients with AGS when alternatives are available, per one expert (personal communication).
It’s important to understand that sometimes the benefit of a vaccine outweighs the risk of a reaction, for example, a rabies vaccine in the event of a bite from a potentially rabid animal.
Gelatin in vaccines
Based upon agreement between skin and ex vivo testing, MMR and/or varicella vaccines appear to have been the cause of our alpha-gal allergic patient’s vaccine-associated anaphylaxis. We have previously demonstrated that MMR and zoster vaccine can bind and deplete sIgE to alpha-gal. We now show that MMRV and varicella vaccine also demonstrate binding and depletion of alpha-gal sIgE.
__________
Both this alpha-gal allergic child and our previous alpha-gal allergic adult who reacted to alpha-gal/gelatin-containing vaccines had low serum concentrations of gelatin sIgE.
__________
Notably, alpha-gal allergic patients have been reported to react to gelatin even with negative gelatin sIgE.
| Vaccine type | Contain gelatin | Do NOT contain gelatin (may contain other mammal-derived excipients or residues or be made in mammalian cell lines) |
| Flu (for 2025)** | Flumist Quantity per dose: 2 mg |
*Flulaval quadrivalent *Fluzone quad and high-dose *Flublok quad *Afluria *Fluarix *Fluad |
| MMR |
• MMR II (measles, mumps, rubella)
• ProQuad (measles, mumps, rubella, varicella) |
*Priorix |
| Varicella zoster | Zostavax (not currently available in the U.S.) | *Shingrix |
| Varicella zoster | Varivax Quantity per dose: 8.9-12.5 mg |
? |
| Typhoid | Vivotif (oral Typhoid) Quantity per dose: Gelatin capsule |
Typhim Vi |
| Rabies | Rabavert Quantity per dose: ≤ 12 mg |
Imovax |
| Yellow fever | YF-Vax Quantity per dose: not specified |
Stamaril |
| Covid†† | *Moderna *Pfizer (Cominarty) * Novavax (Nuvaxovid) |
|
| Tetanus/TDaP*** | †Adacel *Tenivac (Tetanus, Diphtheria) |
|
| RSV††† | Arexvy Abrysvo |
|
| Meningitis | Menveo Trumenba |
|
| Pneumococcal‡ | *Pneumovax 23 *Prevnar 20 |
* At least one expert reports anecdotally that overall, the majority of their patients with AGS who have received this product thus far have reported that they tolerated it (personal communication).
** At least one expert recommends that their patients with AGS avoid Flucelvax, as they have seen reactions in their clinic (personal communication).
*** At least one expert recommends that their patients with AGS avoid Boostrix, as they have seen reactions in their clinic (personal communication).
† At least one expert notes that while the majority of their patients with AGS who have received Adacel thus far have reported that they tolerated it, it contains bovine casamino acid as stabilizer, which is a mammal-derived ingredient (personal communication).
†† At least one expert notes that the majority of their patients with AGS who have received mRNA vaccines thus far have reported that they tolerated them. Cominarty (Pfizer) seems to be alpha-gal-safe. Moderna’s Spikevax appears AG-safe, as does Nuvaxovid (personal communication).
††† At least one expert notes that the majority of their patients with AGS who have received the above RSV vaccines thus far have reported that they tolerated them (personal communication).
‡ At least one expert notes that there is still not a lot of information, but that the majority of their patients with AGS who have received the above pneumococcal vaccines thus far have reported that they tolerated them (personal communication).
Sources:
- The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. Vaccine Ingredients: Gelatin. Accessed February 25, 2025. https://www.chop.edu/vaccine-education-center/vaccine-safety/vaccine-ingredients/gelatin
- Excipients in Vaccines Not Routinely Recommended in the US. Institute for Vaccine Safety – Information on vaccine safety. Published January 21, 2025. Accessed February 2, 2025. https://www.vaccinesafety.edu/excipients-in-vaccines-not-routine/
Warning and disclaimer
- This information is incomplete.
- Some vaccines that do not contain gelatin may contain other sources of alpha-gal, including mammal-derived excipients and residues from the manufacturing process. Moreover, some may be made in mammalian cell lines.
- You must confirm this information. We have done our best to provide accurate information, but we are not medical professionals and cannot guarantee its accuracy. It is the provider’s responsibility to confirm the content of vaccines and determine their safety for individual patients.
- This information does NOT constitute a recommendation or medical advice.
If you are a patient, please seek the advice of a physician about vaccine decisions.
Graded dosing
Summary Statement 9: In a patient with a history and skin test results consistent with an IgE-mediated reaction to a vaccine who requires additional doses of the suspect vaccine or other vaccines with common ingredients, consideration can be given to administering the vaccine in graded doses under observation. (C)
If vaccine or vaccine component skin test results are positive, the vaccine might still be administered, if necessary, in graded doses (Table V). If the full vaccine dose is normally a volume of 0.5 mL, the patient is first given 0.05 mL of a 1:10 dilution and then given full-strength vaccine (at 15-minute intervals) at doses of 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, and finally 0.2 mL, for a cumulative dose of 0.5 mL.
This procedure in a patient who is presumed to be allergic to the vaccine being administered needs to be performed under direct medical supervision, with emergency medications and equipment immediately available to promptly treat an anaphylactic reaction should it occur. Such challenges can be performed in an office or hospital setting with or without an intravenous line in place, depending on the severity of the original reaction to the vaccine and the patient’s medical condition.
See the below vaccine parameter update for more information:
- Kelso JM, Greenhawt MJ, Li JT, et al. Adverse reactions to vaccines practice parameter 2012 update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130(1):25-43.
- Kelso JM. The adverse reactions to vaccines practice parameter 10 years on—what have we learned? Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. Published online January 31, 2022. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2022.01.026
More information
From Pill Clarity:
- Is the COVID-19 Vaccine Vegan?*
* Note that this article does not reflect that we confirmed, via the Swedish Medical Association, that the Pfizer Covid vaccine has no detectable casein in the final product.
Select publications
on AGS and vaccines
- Chiu CY, Henao-Martínez AF, Higuita NIA. Incidence of anaphylaxis in patients with alpha-gal syndrome receiving gelatin-containing vaccines: A large database analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2024;0(0). doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2024.11.010
- Leong S, Lee J. DELAYED DIFFUSE HIVES AFTER VACCINES IN ADOLESCENT WITH POSITIVE ALPHA-GAL IGE AND GELATIN SKIN TEST. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023;131(5, Supplement 1):S110-S111.
- Zafar S, Wolff A, Schutzer S, McGintee E, Torre A. Are gelatin-containing vaccines safe to give in alpha-gal sensitized patients? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149(2):AB99.
- Kelso JM. The adverse reactions to vaccines practice parameter 10 years on—what have we learned? Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. Published online January 31, 2022. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2022.01.026
- Schmidle P, Mehlich J, Brockow K, Darsow U, Biedermann T, Eberlein B. Gelatin-Containing Vaccines for Varicella, Zoster, Measles, Mumps, and Rubella Induce Basophil Activation in Patients with Alpha-Gal Syndrome. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. Published online March 18, 2021:1-7.
- Caballero ML, Krantz MS, Quirce S, Phillips E, Stone CA Jr. Hidden Dangers: Recognizing Excipients as Potential Causes of Drug and Vaccine Hypersensitivity Reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. Published online March 15, 2021. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2021.03.002
- Stone CA Jr, Commins SP, Choudhary S, et al. Anaphylaxis after vaccination in a pediatric patient: further implicating alpha-gal allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7(1):322-324.e2.
- Akella K, Patel H, Wai J, Roppelt H, Capone D. Alpha Gal-Induced Anaphylaxis to Herpes Zoster Vaccination. Chest. 2017;152(4):A6.
- Stone CA Jr, Hemler JA, Commins SP, et al. Anaphylaxis after zoster vaccine: Implicating alpha-gal allergy as a possible mechanism. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(5):1710-1713.e2.